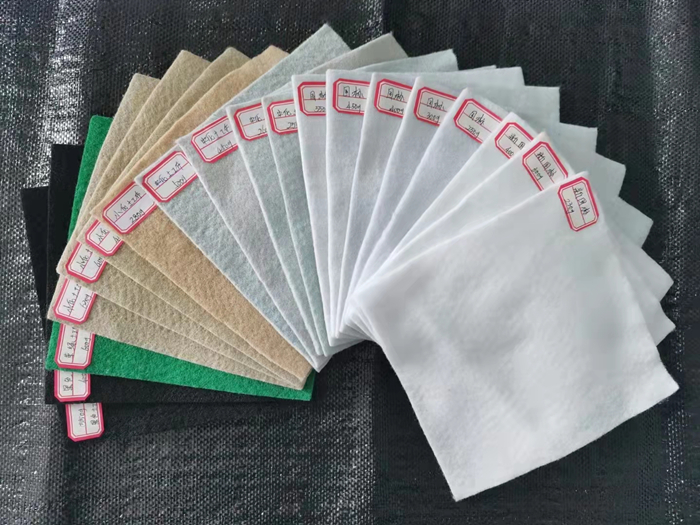





Dustproof geotextile商品描述



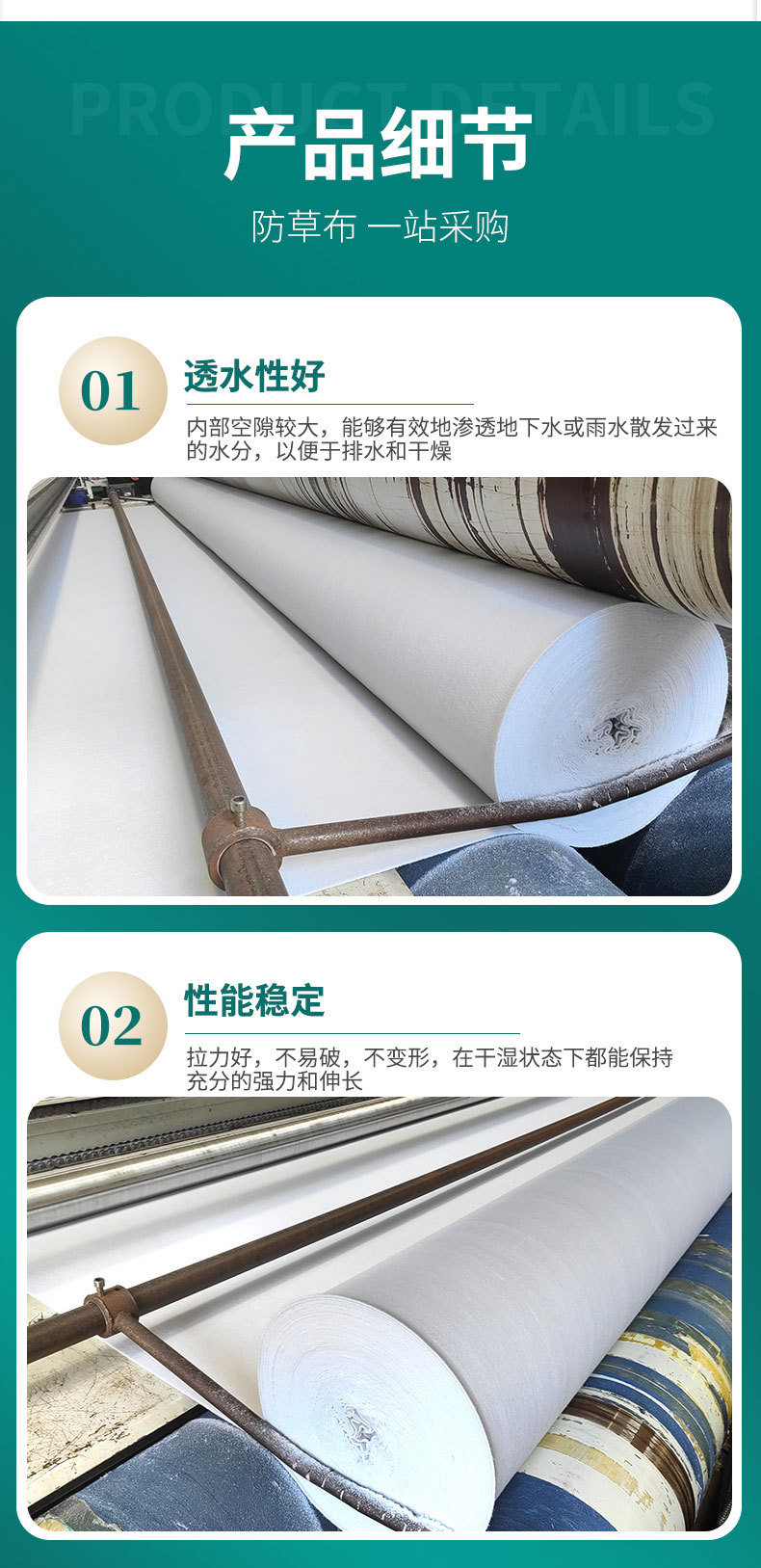


Characteristics of dustproof geotextile:
Strength - Under the same weight specifications, the tensile strength in all directions is higher than other needle punched non-woven fabrics;
Anti UV light exposure - with extremely high UV resistance;
Extreme high temperature resistance - able to withstand high temperatures up to 230 ℃, maintaining structural integrity and original physical
properties at high temperatures;
Permeability and plane drainage - Geotextiles are thick and needle punched, with good plane drainage and vertical permeability, and can still
maintain this performance after many years;
Creep resistance - Geotextiles have better creep resistance than other geotextiles, therefore they have good long-term performance. It can
withstand the erosion of common chemical substances in soil and the corrosion of gasoline, diesel, etc;
Ductility - Geotextiles have good elongation under certain stress, allowing them to adapt to uneven and irregular base surfaces;
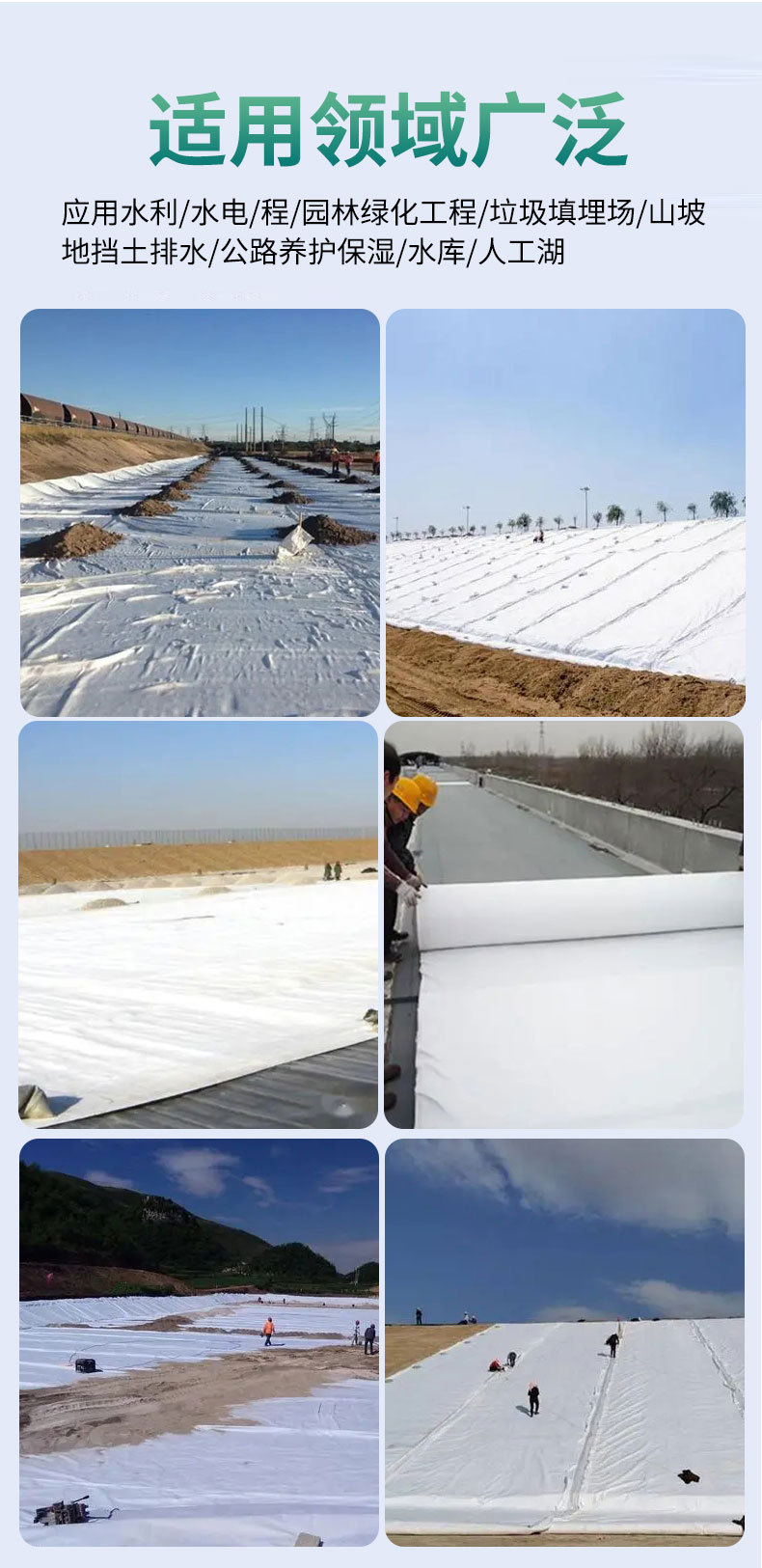
Application field of dust-proof geotextile
(1) Reinforce the backfill of retaining walls or use panels to anchor retaining walls. Construct enclosed retaining walls or bridge piers.
(2) Strengthen the flexible pavement, repair cracks on the road, and prevent reflection cracks on the pavement.
(3) Enhance the stability of gravel slopes and reinforced soil to prevent soil erosion and freezing damage to the soil at low temperatures.
(4) The isolation layer between the ballast and the roadbed, or the isolation layer between the roadbed and the soft foundation.
(5) The isolation layer between artificial fill, stone or material fields and the foundation, the isolation between different frozen soil layers, and the
filtering and reinforcement effects.
(6) The filter layer of the upstream dam surface of the ash storage dam or tailings dam, and the filter layer of the drainage system in the backfill
soil of the retaining wall.
(7) The filter layer around the drainage pipe or gravel drainage ditch.
(8) The filter layer of water wells, relief wells, or inclined pressure pipes in hydraulic engineering.
(9) The geotextile isolation layer between highways, airports, railway ballast, and artificial rock piles and the foundation.
(10) Vertical or horizontal drainage inside the earth dam, buried in the soil to dissipate pore water pressure.
(11) Drainage behind the anti-seepage geomembrane or under the concrete protective surface in earth dams or embankments.
(12) Eliminate water seepage around the tunnel, reduce the external water pressure borne by the lining, and alleviate water seepage around
various buildings.
(13) Drainage of artificial fill foundation for sports field foundation.
(14) Used to strengthen weak foundations in highways (including temporary roads), railways, embankments, earth rock dams, airports, sports fields,
and other engineering projects.
上一篇: Previous:Short Fiber Geotextile
下一篇:Next:Anti-seepage geotextile
- 11-26Production process of composite geomembrane
- 11-26Application of Grass proof Cloth
- 11-26Why is artificial lake anti-seepage membrane suitable for reservoir construction
- 11-26Application of composite geomembrane in reservoirs
- 11-26The role of impermeable membrane in aquaculture
- 11-26Characteristics and functions of geotextile
- 1What is waterproof geotextile
- 2Will geomembranes pollute the environment?
- 3Classification of Geotextiles
- 4The function and construction method of geomembrane
- 5Characteristics and functions of geotextile
- 6Installation of garage roof drainage board
- 7Application of Grass proof Cloth
- 8The difference between geomembrane and composite geomembrane
- 9Key points of geomembrane welding
- 10The use of composite geomembrane
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English






